Introduction to Why Should I Buy Cryptocurrency :
Cryptocurrency is a conception that has become more familiar in financial conversations . It consults to digital or virtual currencies that utilise cryptography to guarantee transactions and administer the generation of new units dissimilar familiar currencies reissued by authorities and central banks, cryptocurrencies run on decentralised net works created on digital ledger tech .
Blockchain is a distributed database system that records transactions across numerous computers in a transparent and irreversible manner. This technology underpins cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many others, allowing transactions to take place without the need for brokers like as banks.
The establishment of Bitcoin in 2009 by an unnamed individual or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto signalled the start of the cryptocurrency revolution. Bitcoin, sometimes known as “digital gold,” gained popularity as a decentralised digital currency with a finite supply, intended to address the shortcomings of traditional fiat currencies such as inflation and central control.
One of the key benefits of cryptocurrencies is their ability to disrupt existing financial institutions. Cryptocurrencies try to democratise finance and promote financial inclusion to the uninsured and underbanked by removing brokers and enabling direct transactions between individuals.
Furthermore, the why should i buy cryptocurrencies by mainstream businesses and organisations has helped recognise them as acceptable financial assets. Major corporations including as Tesla, Square, and PayPal have integrated cryptocurrencies into their operations, boosting acceptance and investor trust.
Given problems such as regulatory uncertainty and price volatility, cryptocurrencies remain popular as an alternative investment class. Investors are attracted to the prospect for high returns, diversification benefits, and exposure to cutting-edge technology driving the digital economy.

2. Potential For High Returns:
Cryptocurrencies have attracted a lot of interest due to their ability to create large returns, frequently exceeding traditional investing alternatives. Here’s a closer look at why investors get drawn to the profitable chances presented by cryptocurrency.
(1) Historical Performance:
Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum have shown outstanding profits over time. For example, Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, began with a tiny value and rose to an all-time high of more than $60,000 in 2021, showing its exponential development.
(2) Market Volatility:
While volatility is frequently listed as a danger factor, it may also provide opportunities for traders and investors. The cryptocurrency market’s volatility may cause quick price swings, opening up potential for short-term gains through trading methods such as day trading and swing trading.
(3) Getting Trends and Technologies:
The bitcoin market is continuously changing, with fresh efforts and ideas appearing. Investing in promising businesses and developing technologies such as decentralised finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and blockchain-based solutions can offer considerable rewards as these industries expand and learn mainstream usage.
(4) Limited Supply & Scarcity:
Many cryptocurrencies have a limited supply, with a specified maximum token or coin issue. Bitcoin, for example, has a finite supply of 21 million coins, resulting in scarcity and potentially increasing its value as demand grows.
(5) Global Demand and Adoption:
The growing global demand for cryptocurrencies, driven by causes such as economic uncertainties, inflationary pressures, and technology breakthroughs, adds to their potential for significant profits. As more people, businesses, and institutions adopt cryptocurrencies, the market demand and value proposition increase.
(6) Speculative Nature:
It’s essential to recognise that the cryptocurrency market is influenced by speculation and market emotion. Positive news, legislative reforms, and technology advancements might cause price increases, pulling investors looking for rapid returns.
(7) Differences Benefits:
Including cryptocurrencies in an investing portfolio may give variation, especially when traditional markets are unstable or down. Cryptocurrencies frequently have minimal correlations with traditional asset classes such as equities and bonds, providing a buffer against market risks.
Regarding the potential for significant rewards, cryptocurrency investors must proceed with care and undertake extensive study. To make sound investment selections, consider market volatility, regulatory changes, security threats, and project fundamentals.
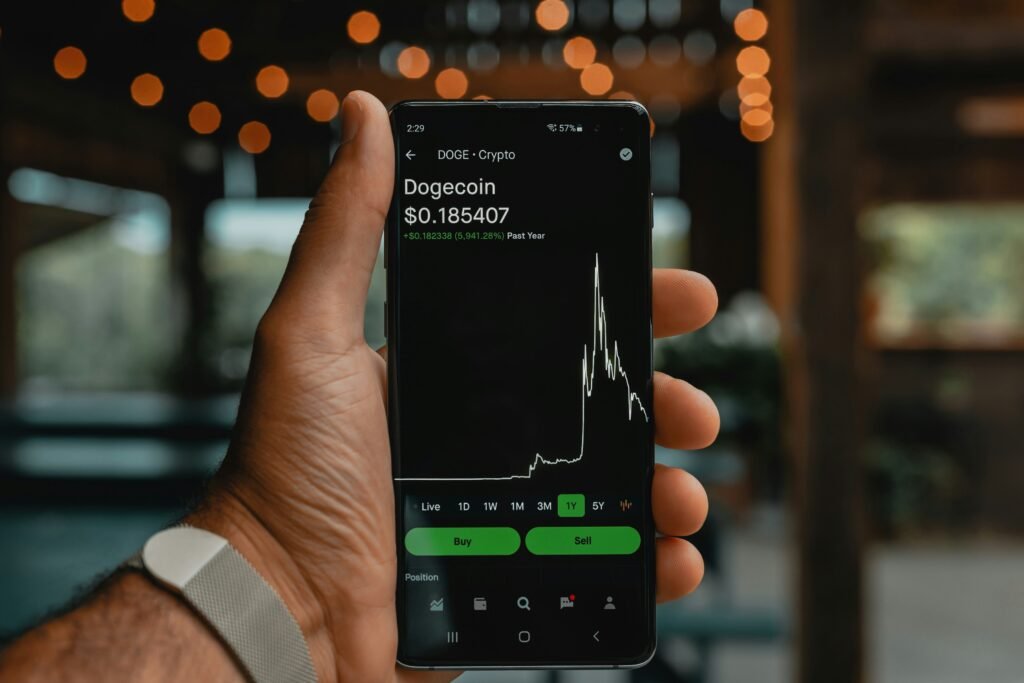
3. The diversification Benefits:
Diversity is a key idea in investing strategy that seeks to reduce risk by distributing assets across many asset types. Adding cryptocurrency to your financial portfolio can provide various diversification benefits:
(1) Struggling Relationship:
Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others have a poor correlation with traditional asset classes including equities, bonds, and real estate. This implies that their price swings are less likely to follow typical market patterns, offering a buffer against market volatility.
(2) Different Asset Classes:
Cryptocurrencies are an alternative asset class that works outside of existing financial systems. By investing in cryptocurrencies, investors receive access to a distinct market with its own dynamics and development potential, broadening their portfolio beyond traditional assets.
(3) Organised Nature :
Unlike traditional financial assets, which are subject to centralised control and regulatory forces, cryptocurrencies run on decentralised networks. This global design decreases reliance on central authorities while also reducing the risks associated with geopolitical events or regulatory changes that may affect traditional markets.
(4) Rise in inflation Protect:
Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin are frequently marketed as inflation insurance due to their restricted supply and negative properties. In times of economic instability or inflationary pressures, the scarcity of cryptocurrencies can protect buying power and act as a store of value, much like gold.
(5) Global Accessibility:
Cryptocurrencies are globally accessible, allowing investors to engage in the digital economy regardless of location. This accessibility is especially useful for diversifying exposure to international markets and capitalising on new trends and opportunities internationally.
(6) Broad Risk Factors:
When cryptocurrencies are included in a diversified portfolio, a new set of risk factors emerges that differs from traditional assets. While cryptocurrencies may be volatile and subject to regulatory risks , their performance may be impacted by variables such as technology improvements, market mood, and adoption patterns, hence broadening the portfolio’s risk profile.
(7) Potential for development and Innovation:
The cryptocurrency market’s dynamic nature creates potential for development and innovation. Investments in blockchain technology, decentralised finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and other developing areas can help to diversify your portfolio while also capitalising on creative advances.
When introducing cryptocurrencies into their portfolio, investors should examine their risk tolerance, investing objectives, and time horizon. Diversification should be undertaken carefully, taking into consideration the distinct features and risks associated with each asset type.

4. Technology And Innovative Ideas:
Cryptocurrencies are at the forefront of innovation, pushing huge technological developments and altering whole sectors. Here are some major elements highlighting the innovation and technological development related with cryptocurrency:
(1) Blockchain Technology:
A decentralised and immutable the register system, enables secure and transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries. In addition to cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology has applications in supply chain management, healthcare, voting systems, and other areas, revolutionising data integrity and trust in digital interactions.
(2) Advanced Agreements:
Automate agreements enforcement, streamline processes, and eliminate middlemen in contractual interactions. They are essential for the creation of decentralised applications (DApps) and the growth of decentralised financial platforms (DeFi).
(3) Decentralised Finance (DeFi):
DeFi is an important development in financial services that uses blockchain and cryptocurrency technology to offer decentralised alternatives to traditional banking and financial institutions. DeFi systems include services including financing, borrowing, trading, and yield farming, giving consumers more control over their funds and access to global markets.
(4) Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs):
NFT are distinct digital assets that indicate ownership or proof of the authenticity of digital property, such as artwork, things like and virtual real estate. Based on blockchain technology, NFTs allow producers and collectors to tokenize and trade digital assets, opening up new revenue streams and opportunities in the digital economy.
(5) Connectivity and Cross-Chain Solutions:
Connectivity innovations seek to bridge disparate blockchain networks, allowing for the effortless flow of assets and data between protocols. Cross-chain solutions improve scalability, efficiency, and connection in the blockchain ecosystem, encouraging collaboration and integration of various blockchain platforms.
(6) Scalability Solutions:
Scalability is a significant difficulty in blockchain technology, especially as networks struggle to handle an increasing user base and transaction volume. Scalability concerns and blockchain network performance are being addressed by innovations such as layer-2 solutions, dividing, and consensus techniques like as proof-of-stake (PoS) and proof-of-authority (PoA).
(7) Privacy and Security:
Cryptocurrencies prioritise privacy and security using cryptographic techniques such as encryption and zero-knowledge proofs. Privacy-focused cryptocurrencies and protocols improve user anonymity and data security, ensuring secrecy in digital transactions and communications.
(8) Environmental Sustainability:
The environmental effect of cryptocurrency mining has inspired innovation in sustainable blockchain solutions. Projects are looking at energy-efficient consensus algorithms, renewable energy sources for mining activities, and carbon offset schemes to address environmental concerns about blockchain technology.
5. Global Accessibility and Financial Inclusion:
Cryptocurrencies have emerged as an effective instrument for advancing global financial inclusion, providing individuals with access and empowerment throughout the world. Here’s a look at how cryptocurrencies improve global accessibility and financial inclusion:
(1) Unlimited Transactions:
Cryptocurrencies allow individuals to send and receive payments across geographical borders without the need of traditional banking infrastructure. This is especially useful for remittance payments, cross-border trade, and international money transfers, which reduce transaction costs and delays associated with traditional banking systems.
(2)Empowering the Unbanked:
According to the World Bank, around 1.7 billion adults worldwide remain unbanked, unable to access formal financial services. Cryptocurrencies enable the unbanked people to join in the digital economy, store and transfer value, have access to savings and credit possibilities, and engage in economic activities without the need for traditional banking accounts.
(3) Reduce banking Limitations:
Traditional banking institutions frequently impose limitations such as minimum balance requirements, transaction fees, and verification requirements, which limit financial inclusion for marginalised people. Cryptocurrencies provide a more inclusive and accessible alternative, allowing people to create digital wallets and engage in financial transactions with low entry barriers.
(4) Empowering Peoples with Management:
Cryptocurrencies provide individuals with more autonomy over their resources. Users hold their private keys, which allows them to manage and protect their digital assets individually. This financial liberty is especially important in areas with volatile or restrictive banking systems, political uncertainty, or limited access to traditional financial services.
(5) Microtransactions and Micropayments:
Cryptocurrencies make micropayments and microtransactions possible, allowing for small-value transfers that would be impracticable or prohibitively expensive using standard payment systems. This enables content producers, freelancers, and small enterprises to monetise digital material, services, and goods internationally, promoting economic inclusion and entrepreneurship.
(6) Financial Awareness and Education:
The usage of cryptocurrencies promotes financial education and literacy by teaching users about digital wallets, blockchain technology, and safe methods for handling digital assets. This information enables people to make educated financial decisions, avoid fraud, and efficiently navigate the expanding digital financial world.
(7) Crypto Communities and Peer-to-Peer Networks:
(P2P) networks play an important role in increasing financial inclusion. P2P systems allow for direct transactions between individuals, eliminating intermediaries and enabling financial exchanges based on trust, reputation, and shared values within communities.
(8) Charity Projects and Social Impact:
Cryptocurrencies help charitable organisations and social impact projects by employing blockchain transparency and traceability to track donations and ensure accountability. Cryptocurrency donations may help underserved areas, promote humanitarian projects, and generate good social change throughout the world.
6. Risks and Concerns:
(1) Industry Fluctuation :
The tag instability of cryptocurrencies is famous, with information fluctuating dramatically over concise periods of time . Such volatility links to speedy tag swings, that can bear on investor sentiment and portfolio worth . Investors have to gain a extended investment method and be ready for tag fluctuations to decrease the effect of industry volatility.
(2) Legal Risk:
Each country and area has its own set of legislation regarding cryptocurrencies. Government actions, policy decisions, and regulatory changes can all have an influence on cryptocurrency use, trading, and legality. Investors must to monitor regulatory changes and evaluate the regulatory risks related to the investments they make.
(3) Security and Risk :
Risks to security for cryptocurrencies include hacking, cyberattacks, and theft. Exchange hacks, phishing schemes, and wallet flaws can all lead to the loss of cash. It is critical for investors to establish strong security measures, including as utilising renowned exchanges, enabling two-factor authentication, and keeping bitcoins in safe hardware wallets.
(4) Liquidity Risks:
Some cryptocurrencies may have liquidity issues, particularly less popular or recently issued coins. Low liquidity might make it difficult to purchase or sell cryptocurrencies at the appropriate price, resulting in price overrun and decreased trading efficiency. When trading or investing in cryptocurrency, investors should consider liquidity.
5. Technological Risks:
Blockchain technology is still growing, and cryptocurrencies may experience capacity, network congestion, and software problems. Forks in blockchain protocols, software upgrades, and changes to consensus mechanisms can all have an influence on cryptocurrencies’ stability and operation. Investors should remain current on technology changes and evaluate the technical risks connected with cryptocurrencies.
6. Industry Control:
Cryptocurrency markets are subject to manipulation, including pump-and-dump schemes, price manipulation methods, and phoney trading volumes. Manipulation can cause market prices to fluctuate and mislead investors.Investors should take caution, do due research, and avoid falling prey to fraudulent schemes and market manipulation techniques.
7. Tax and regulatory compliance:
Depending on local tax laws and reporting requirements, cryptocurrency investments may be subject to taxation. The capital gains tax, income tax, and reporting requirements for cryptocurrency transactions different by country. Investors should engage with tax specialists and follow tax laws to guarantee accurate tax reporting and compliance.
8. Trade Probability :
Investing in cryptocurrencies, like any other investment, has risks like as capital loss . industry mood, economic considerations, geopolitical events, and investment behaviour all have the capabilities to affect cryptocurrency prices . Investors have to assess their likelihood open- theirmindedness, diversify their investment portfolio, and bypass from investing over they have the ability to afford to lose .
9. Growing Risks as well as Unanticipated Elements:
The cryptocurrency industry is constantly shifting and dynamic with new threats and undiscovered factors that may impact investment outcomes. Emerging technologies, regulatory changes, market sentiment shifts, and macroeconomic events can all result in new risks and difficulties.Investors should be watchful, react to market fluctuations, and regularly assess their investing strategy.
In Conclusion:
While cryptocurrencies may provide potential benefits and financial possibilities, they also carry risks and concerns that investors should carefully analyse. Understanding and efficiently managing these risks allows investors to make more informed decisions and navigate the bitcoin market with more confidence.

